The roof must withstand heavy loads. To give it a fortress, a special construction is arranged, which consists of roof trusses and crates. Its purpose is to transfer the load from the weight of the roof and snow cover to the internal supports of the structure. Rafter rafters are used in buildings with small spans or in structures with an average bearing wall or intermediate supports. If there are none, then the design of the hanging rafters is used.
Content
Rules and subtleties of the device of outdoor rafters
It is possible to cover the span with the roof truss structure, the maximum length of which is from 6 to 6.5 meters. Provided that inside the building there can be such load-bearing structures as columns or walls, there is an additional opportunity to install racks on them.
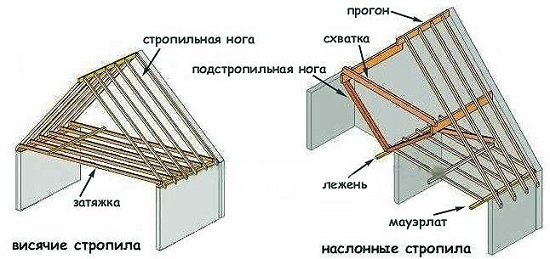
Since large spans are found in private construction quite rarely, then in individual buildings mainly rafters are used.
According to the technology, the rafter leg rests on the Mauerlat (in the case of a wooden building, its function is transferred to the upper row of the wall). This nodal connection is considered particularly important.
If the rafter legs are pulled together with a crossbar, then the span can be increased to 8 m, with one support - up to 12 m, using two supports - up to 16 meters.

Do not lay wooden rafters on stone walls. They constantly form condensation, which will destroy the tree. So that it does not rot, the Mauerlat must be insulated. The same must be done in all places where the tree is adjacent to structures made of stone or metal. As an insulating material, roofing material in 2 layers or a similar material is used.
During the installation of a layered roofing system, the correct fixing of the rafters on the rafter bar deserves special attention.
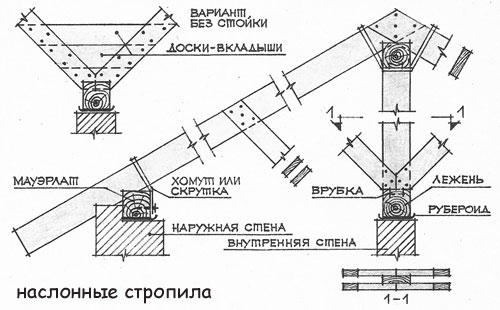
First of all, you need to securely fasten the Mauerlat. It is a beam with sides measuring 140-160 mm. This is done using metal pins, which are concreted into the wall by at least 40 cm. In the same way, bolts can be fixed.
For this purpose, wire twists with a diameter of at least 6 mm can be used. They are laid during the construction of walls no higher than in the third row of masonry, counting from the top edge.
The roof rafters can be attached to the Mauerlat using staples. The bar, which is placed on top of the internal exterior structures and is called “lying”, has similar requirements.
During the construction of houses, roof rafters made of wood are used. The use of such elements of metal or reinforced concrete does not justify itself and, in general, is difficult to implement.
It is convenient to use joints in the form of spikes, teeth and pans, which are widely used in carpentry, to connect and fasten wooden scaffolds, support bars and other details.
The layered system, the design of which withstands the pressure of the roofing cake and itself, must be well-designed even before the rafters are laid.
When the log houses of the houses have not yet dried well, and their complete shrinkage has not occurred, the installation of the supporting roof structures must be done especially carefully.

Remember that with the shrinkage coefficient of a log house (made of logs or beams and having a height of 3 meters), which is 4-6%, the house can sit 10-20 cm per year.This may damage the load-bearing elements of the roof and inserted carpentry. That is why it is customary to lay the dimensions of the house in the project in two versions - initial and after shrinkage.
One solution to the problem may be the use of hanging rafter systems. Otherwise you have to
- expect the final shrinkage of the house,
- use rafters that have sliding supports,
- strengthen all supporting structures by substituting screw jacks as shrink compensators.
In the first case, the disadvantage is a long wait, in the latter - it requires high professional skills and accuracy during manual work. But the use of sliding mounts, which can be considered self-regulating, provides additional advantages.
For example, the sliding structure perfectly compensates for the property of wood to shrink and the ability to “breathe” and deform (albeit slightly) throughout its entire service life.
This design is done as follows: on a Mauerlat, a bar is stuffed at the right angle or cutting of the desired shape is made. Then a corner is attached to it, one shelf of which is bent. Under the bend they pass the working embossed plate.

The plate on the rafters is fixed so that in the direction of the ridge of the house there is a significant distance for free sliding, which occurs to the outside.
When purchasing a joint for sliding, you need to know that it can be of a different working size (the supporting platforms of the plates are at different distances). You need to choose it, taking into account the planned degree of shrinkage of the building. At the same time, it is noted that the size distribution of shrinkage will occur on the rafters of two slopes.

The emphasis of the rafters on the rafter beam is not the only movable node of the rafter structure. The ridge also needs some type of swivel device. Rafter rafters can be butt-joined using metal plates. A significant angle is left from the end. It does not allow the rafters to abut each other during convergence. You can use another option, when the rafters are connected to the overlay. In this case, holes are made in both legs through which the bolt passes.
Construction of rafters
The rafter system, in which the upper assembly is mounted using a hinge, and the lower one using a hinge and a floating connection (the option of a slider was described above), it is customary to call indisputable. In such a system, loads are not transferred to the Mauerlat, and through it to the walls.
In contrast to them, the ridge connection is rigidly performed in the spacer system, and the Mauerlat is supported by a hinge (as an option, the connection is “tooth”). In this case, parting forces are transmitted to the walls.
Such a system, which combines the lay and hanging rafters, can be considered hybrid.
In this case, the load is redistributed. The weight of the roof is taken solely by the rafters, which are butt-joined and bend. In this case, the ridge beam ceases to be an indispensable element of the rafter system, since it is practically inactive.

When the spacer circuit is especially important to consider the quality of the bolted connections. They are produced using pre-drilled holes, the diameter of which should be 1 millimeter smaller than the diameter of the stud or bolt. If they are excessively large, damage to the Mauerlat may occur during the selection of the freewheeling part.
The operation of the rafters will differ depending on which of the rafter joints will work in hard mode and which will be articulated.
When the operation of the roof occurs under normal conditions, without overloads, then the entire load that the rafter system experiences is evenly distributed over all its elements.But with the advent of winter and snowfall, each slope has a different load. In the case of poorly fixed or improperly mounted racks, a roof shift to the side of an overloaded ramp can occur. The possibility of such a bias is most likely when it comes to an indisputable scheme. The problem can be prevented if the ridge beam is securely fixed, excluding its longitudinal shifts.
In what order is the rafters made
The technological process of the roof device consists of the following steps:
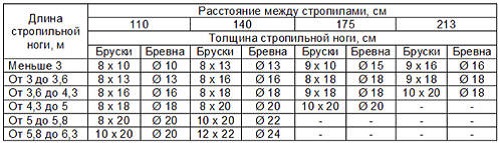
- The table below makes it possible to calculate the cross section of the rafter legs, starting from their length;
- In the case where there is no lumber that would have the required length and thickness according to the project, they can be obtained by splicing with screws or nails;
- It is necessary to make a rafter template, and if the design consists of racks and struts, it would be nice to make templates for them;

Remember that when installing hip roofs, which basically have 4 slopes, it is important to take into account some peculiarity. The length of the rafters, which are located in the place where the rajets are closed, should decrease as they descend from the ridge towards the Mauerlat. It is called a diagonal rafter foot or a slant leg. Since the hip roof has a complex structure, patterns in this case are made for slope elements, which are the main ones. All other elements have to be assembled and customized directly on the spot.
- Prepared and fitted materials rise to the roof;
- Installation begins with racks and a ridge beam (run) - this is done when they are provided for by the project. For greater certainty, it would be nice to additionally attach the racks to the supporting structures of the structure. Such measures will prevent possible but undesirable shifts;
- Given the above rules, in the future, the rafters are installed to the fasteners and fixed in the most suitable way to the Mauerlat. In places of the upper connection, they are attached to the ridge beam or fixed to each other;
- In the case when the project provides for the use of horizontal contractions (which to some extent unites the roof and hanging rafters), then at this stage they are fastened;
- In the future, the installation of struts, trusses and other supporting elements;
- Then a plumb line is produced, which is affected by the roof structure and the length of the rafter legs; All kinds of precipitation can fall on the lower part of the building envelope (walls). To prevent this from happening, the roof is constructed so that in most buildings it extends beyond the outer walls to a distance of at least 50 cm. If the rafters are supported on the Mauerlat using a tooth or a spike, to their lower edge, located on the side, in order to lengthen a special element is beaten - the filly.
- In the case when the project provides for the installation of filly, they must be sheathed around the entire perimeter of the house with a solid wooden crate.
The next stage, when the roof rafters, the design of which was considered above, are sheathed with a crate, is the last before the production of the roofing cake. It includes a vapor barrier, waterproofing device, as well as work on insulation and roofing.


Alas, no comments yet. Be the first!